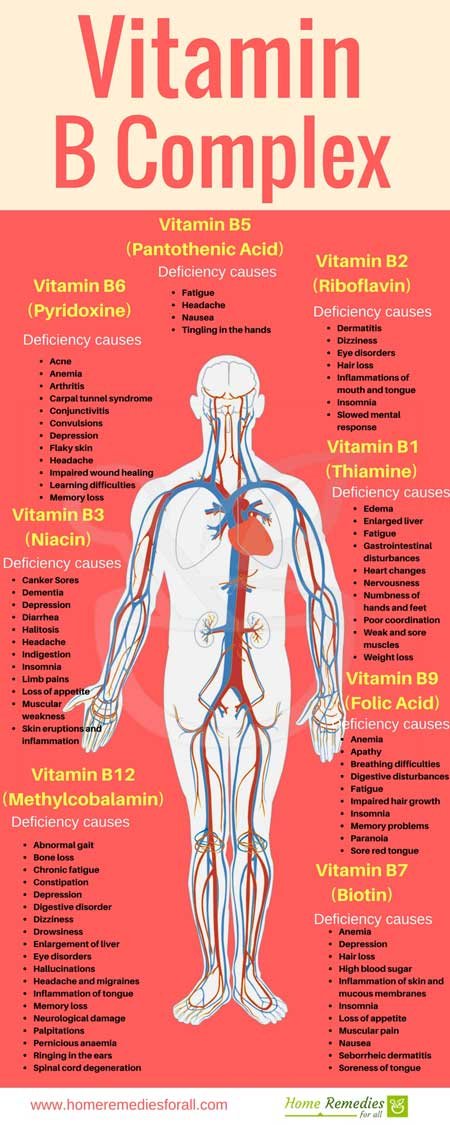
Vitamin B complex is a combination of many B Vitamins including Thiamine (B1), Riboflavin(B2), Niacin (B3), Pantothenic Acid (B5), Pyridoxine (B6), Biotin (B7), Folic Acid (B9) and Cobalamin (B12). They are found in leafy greens, beans, whole grains, dairy and meat. Vitamin B Complex helps to maintain the health of skin, eyes, hair, nerve, liver and mouth. They also help in proper brain functioning and provide healthy muscle tone in the gastrointestinal tract.
The Benefits of Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin B Complex is a group of 8 vitamins used for prevention of vitamin deficiencies due to poor diet, illness, alcoholism and pregnancy. Following are details of each of the 8 vitamin b which are individually essential for certain body functions.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) Thiamine Hydrochloride
- Enhances blood circulation
- Assists in blood formation
- Helps in proper digestion
- Optimizes cognitive activities and brain functioning
- Increases learning capacity
- Provides energy
- Improves muscle tomes of intestines, stomach and heart
- Acts as anti-aging agent
Deficiency of Vitamin B1 can cause
- Beriberi - a nervous system disease
- Constipation
- Edema
- Enlarged liver
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Heart changes
- Irritability
- Loss of appetite
- Nervousness
- Numbness of hands and feet
- Pain
- Poor coordination
- Tingling sensations
- Weak and sore muscles
- Weight loss
Food sources of Vitamin B1
- Brown rice
- Eggs yolks
- Fish
- Legumes
- Liver
- Peanuts
- Peas
- Pork
- Wheat germ
- Whole grains
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Aids in red blood cell formation
- Produces antibodies
- Helps in cell respiration and growth
- Alleviates eye fatigue
- Prevents and treats cataract
- Helps in carbohydrate, fats and protein metabolism
- Facilitates use of oxygen by skin, nails and hair tissues
- Reduces dandruff
- Helps development of fetus in pregnancy
Deficiencies of Vitamin B2 can cause
- Cracks and sores at the corners of mouth
- Dermatitis
- Dizziness
- Eye disorders
- Hair loss
- Inflammations of mouth and tongue
- Insomnia
- Retarded growth
- Slowed mental response
- Skin lesions called ariboflavinosis
Food Sources of Vitamin B2
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
- Fish
- Legumes
- Meat
- Milk
- Poultry
- Spinach
- Whole grains
- Yogurt
Vitamin B3 ( Niacin, Nicotinic Acid, Niacinamide)
- Kids in functioning of nervous system
- Helps in metabolism of Carbohydrates fats and proteins
- Involved in normal secretion of bile and stomach fluids
- Synthesizers sex hormones
- Lowers cholesterol and improve blood circulation
- Helpful in Schizophrenia and other mental diseases
Deficiency of Vitamin B3 can Cause
- Canker sores
- Dementia
- Depression
- Diarrhoea
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Halitosis
- Headache
- Indigestion
- Insomnia
- Limb pains
- Loss of appetite
- Low blood sugar
- Muscular weakness
- Pellagra
- Skin eruptions and inflammation
Food Sources of Vitamin B3
- Beef liver
- Brewers yeast
- Broccoli
- Carrots
- Cheese
- Corn flour
- Dandelion Greens
- Dates
- Dates
- Eggs
- Fish
- Milk
- Nuts
- Peanuts
- Pork
- Potatoes
- Rabbit
- Tomatoes
- Wheat germ
- Whole wheat
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Helps in production of adrenaline hormone
- Produces antibodies
- Aids in vitamin utilisation
- Helps convert carbohydrates fats and proteins into energy
- Produces neurotransmitters
- Enhances stamina
- Prevents certain forms of anaemia
- Helps in treating depression and anxiety
Deficiency of Vitamin B5 can Cause
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
- Tingling in the hands
Food Sources of Vitamin B5
- Avocados
- Beef
- Brewers yeast
- Eggs
- Fresh vegetables
- Kidney
- Legumes
- Liver
- Lobster
- Mushrooms
- Nuts
- Pork
- Whole rye flour
- Whole wheat
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Helps normal Brain function
- Reduces water retention
- Produces hydrochloric acid absorption of fat and protein
- Promotes red blood formation
- Maintains Sodium and potassium balance
- Synthesizers RNA and DNA for normal cellular growth
- Helps in antibody production
- Helps in prevention of atherosclerosis
- Helps in reduction of premenstrual symptoms
- Stops formation of kidney stones
- Health treatment of allergy Arthritis and asthma
Deficiency of Vitamin B6 can Cause
- Acne
- Anemia
- Anorexia
- Arthritis
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Conjunctivitis
- Convulsions
- Depression
- Dizziness
- Flaky skin
- Headache
- Impaired wound healing
- Learning difficulties
- Memory loss
- Nausea
- Numbness
- Oily face
- Sore tongue
Food Sources of Vitamin B6
- Banana
- Beans
- Blackstrap molasses
- Brewers yeast
- Carrots
- Eggs
- Fish
- Meat
- Peas
- Spinach
- Soybeans
- Sunflower seeds
- Walnut
- Wheat germ
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
- Aids in cell growth
- Increases fatty acid production
- Helps in metabolism of Carbohydrates fats and proteins
- Assists in utilisation of other B complex vitamins
- Promotes healthy sweat glands, bone marrow and nerve tissue
- Prevents hair loss
Deficiency of Vitamin B7 can Cause
- Anemia
- Depression
- Hair loss
- High blood sugar
- Inflammation of skin and mucous membranes
- Insomnia
- Loss of appetite
- Muscular pain
- Nausea
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Soreness of tongue
Food Sources of Vitamin B7
- Brewers East
- Cooked egg yolks
- Meat
- Milk
- Poultry
- Saltwater fish
- Soybeans
- Whole grains
Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid) Folate, Folacin or pteroylglutamic acid
- Help formation of red blood cells
- Provides energy
- Helps in proper formation and functioning of white blood cells which strengthens immunity
- Helps in protein metabolism
- Treats Folic acid anaemia
- Reduces anxiety and depression
- Helps in treatment of cervical dysplasia
- Regulate homocysteine levels. High levels can cause atherosclerosis
- Helps regulate embryonic and fetal nerve cell formation
Deficiency of Vitamin B9 can Cause
- Anemia
- Apathy
- Breathing difficulties
- Digestive disturbances
- Fatigue
- Impaired hair growth
- Insomnia
- Memory problems
- Paranoia
- Sore red tongue
Food Sources of Vitamin B9
- Asparagus
- Barley
- Beef
- Bran
- Brewers yeast
- Brown rice
- Cheese
- Chicken
- Dates
- Green leafy vegetables
- Lamp
- Legumes
- Lentils
- Liver
- Milk
- Mushrooms
- Orange
- Pork
- Root vegetables
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Wheat germ
- Whole grains
Vitamin B12 (Methylcobalamin)
- Helps growth and protection of nervous system
- Help prevent Parkinson's disease and slows progression in those who already have it
- May help in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases
- Aids folic acid absorption
Deficiency of Vitamin B12 can Cause
- Abnormal gait
- Bone loss
- Chronic fatigue
- Constipation
- Depression
- Digestive disorder
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Enlargement of liver
- Eye disorders
- Hallucinations
- Headache and migraines
- Inflammation of tongue
- Memory loss
- Neurological damage
- Palpitations
- Pernicious anaemia
- Ringing in the ears
- Spinal cord degeneration
Food Sources of Vitamin B12
- Brewers yeast
- Clams
- Eggs
- Herring
- Kidney
- Liver
- Mackerel
- Milk and dairy products
- Sea vegetables such as dulse, kelp, kombu and nori
- Soybeans
Why Should You Use Vitamin B Complex?
If you are a vegetarian or follow a vegan diet then you are almost certain to have Vitamin B deficiency in one form or the other. Similarly pregnant or breastfeeding women need more vitamin B6, B12 and folic acid.
Your need for vitamin b increases as you grow old. People above 50 generally are deficient in vitamin B complex. Certain diseases like celiac disease, Crohn's disease, gastritis and other digestive disorders increase your requirement for vitamin B.
These vitamins fuel energy into you and help you in conditions like depression , anxiety, heart diseases and premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
You need to take vitamin B complex supplements to meet all these requirementshttps://www.homeremediesforall.com/administrator/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&layout=edit&id=786#.
Doctors will generally recommend vitamin B complex supplements in the form of capsules or injections.
Precautions and Tips
Vitamin B complex supplements are water solubles and they do not stay in your body for long. Excess consumption can cause some side effects from individual components. You need to be aware of these side effects and should take doctors help when required.
- Excess consumption of niacin ( Vitamin B3) can increase liver toxicity, elevate blood sugar levels and cause shin pain
- Too much of pyridoxine ( Vitamin B6) can cause nerve damage, impair kidney functioning and increased risks of heart disease, stroke and can even cause death in diabetic patients
- High doses of Vitamin B6 with Vitamin B12 have shown increased incidences of hip fractures
- Overuse of folic acid (Vitamin B9) can cause insulin resistance, damage kidney and even increases risks of certain types of cancers.
- Excess consumption of cobalamin ( Vitamin B12) can impair kidney functioning, increase risks of heart disease
- Higher doses of Vitamin B12 and B9 can increase risks of cancer
Keeping all these aspects in mind it is better to meet your requirements of vitamin B through food which are rich in these vitamins. If a temporary need is created then take supplements under the supervision of a doctor and monitor your deficiency closely. Do not make vitamin B for long periods.

